How Enterprises Build AI Agents in Production
The practical path from demo to production-grade agentic AI systems
Executive Summary
Most enterprise AI agent projects fail not because of model limitations, but because of the gap between demo success and production reality. The Tencent Cloud Agent Development Platform (ADP) team has distilled the complete path for deploying production-grade agentic AI systems—from knowledge cold start to multi-agent orchestration—based on real-world deployments across automotive, hospitality, pharmaceutical, and logistics industries.
Key takeaways:
- An AI agent is not a chatbot, and not every workflow needs an agent
- Knowledge cold start (RAG setup) is where most projects stall
- Multi-agent systems require explicit collaboration patterns, not just multiple prompts
- Enterprise governance (cost, security, audit) is non-negotiable for production
- When choosing an Agent Builder platform, enterprise-grade capabilities matter more than demo performance
1. The Reality Gap: PoC vs Production
Every enterprise AI agent project starts the same way: a successful demo. The model answers questions correctly, stakeholders are impressed, and the project gets approved.
Then reality hits.
A leading automotive manufacturer experienced this firsthand. Their initial chatbot demo handled product inquiries well in controlled tests. But when deployed to real customers:
- Knowledge coverage gaps: Product manuals were complex, with thousands of pages across multiple vehicle models. The system couldn't handle edge cases.
- Cold start delays: Onboarding new product lines took weeks of manual document processing.
- Traditional bot limitations: Rule-based fallbacks couldn't understand nuanced customer intent.
The result? Customer satisfaction dropped, and the project was nearly shelved.
This pattern repeats across industries. The gap isn't about AI capability—it's about enterprise readiness.
2. What is Agentic AI? Defining Enterprise-Grade Agents
Before diving into the build path, let's clarify what we're actually building. The market conflates three distinct concepts:
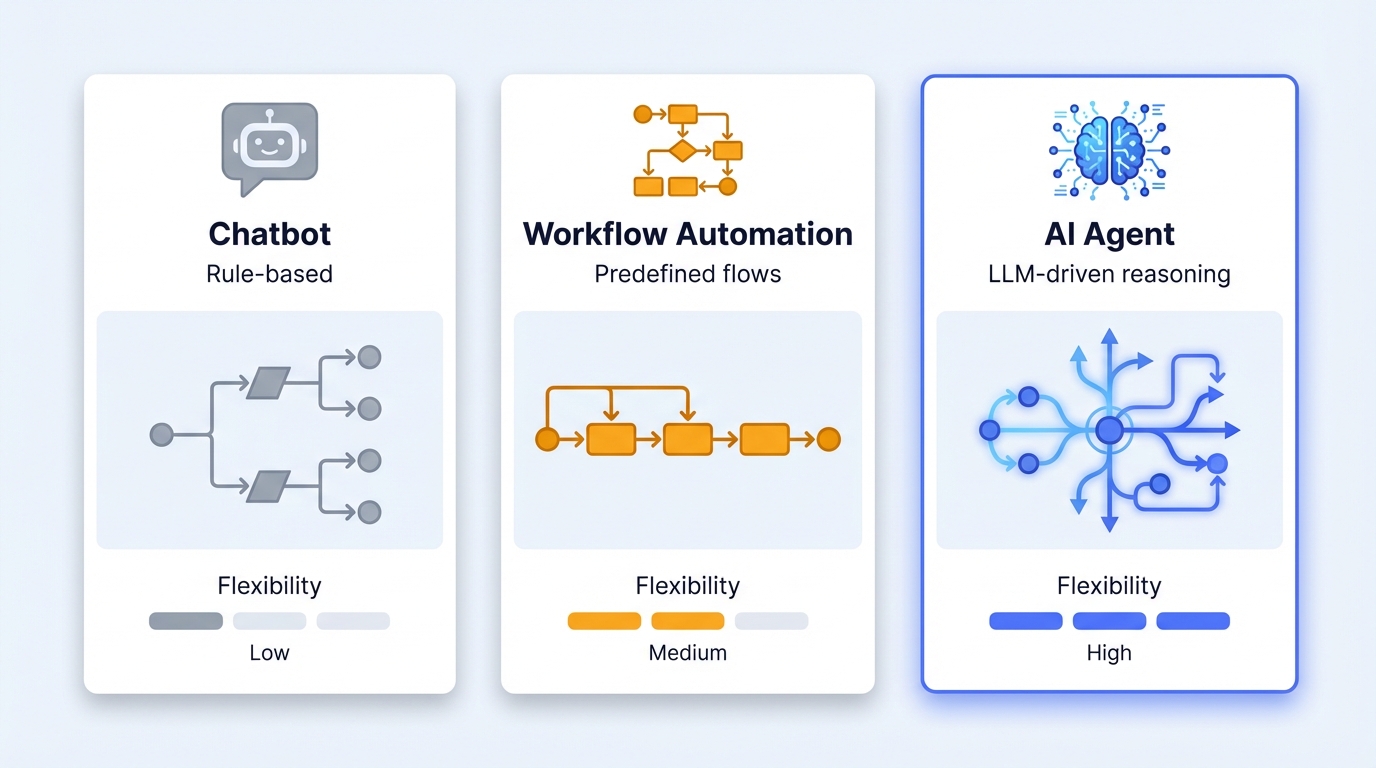
| Dimension | Chatbot | Workflow Automation | AI Agent (Agentic AI) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Decision Logic | Rule-based / Intent matching | Predefined sequence | LLM-driven reasoning, autonomous planning |
| Flexibility | Low (scripted responses) | Medium (branching logic) | High (dynamic decision-making) |
| Knowledge Handling | FAQ lookup | Structured data processing | RAG + unstructured knowledge |
| Best For | High-volume, simple queries | Repeatable business processes | Complex, context-dependent tasks |
| Failure Mode | "I don't understand" | Process breaks on exceptions | Hallucination, cost overrun |
The defining characteristic of agentic AI is autonomy—agents can independently plan steps toward a goal, invoke tools, and handle exceptions rather than following preset scripts. This is why agentic AI has become the core direction for enterprise AI deployment in 2025.
The enterprise decision framework:
- Use a chatbot when queries are predictable and volume is high (e.g., order status checks)
- Use workflow automation when the process is well-defined and exceptions are rare (e.g., invoice processing)
- Use an AI agent when tasks require reasoning across unstructured knowledge and dynamic decision-making (e.g., technical support, policy Q&A)
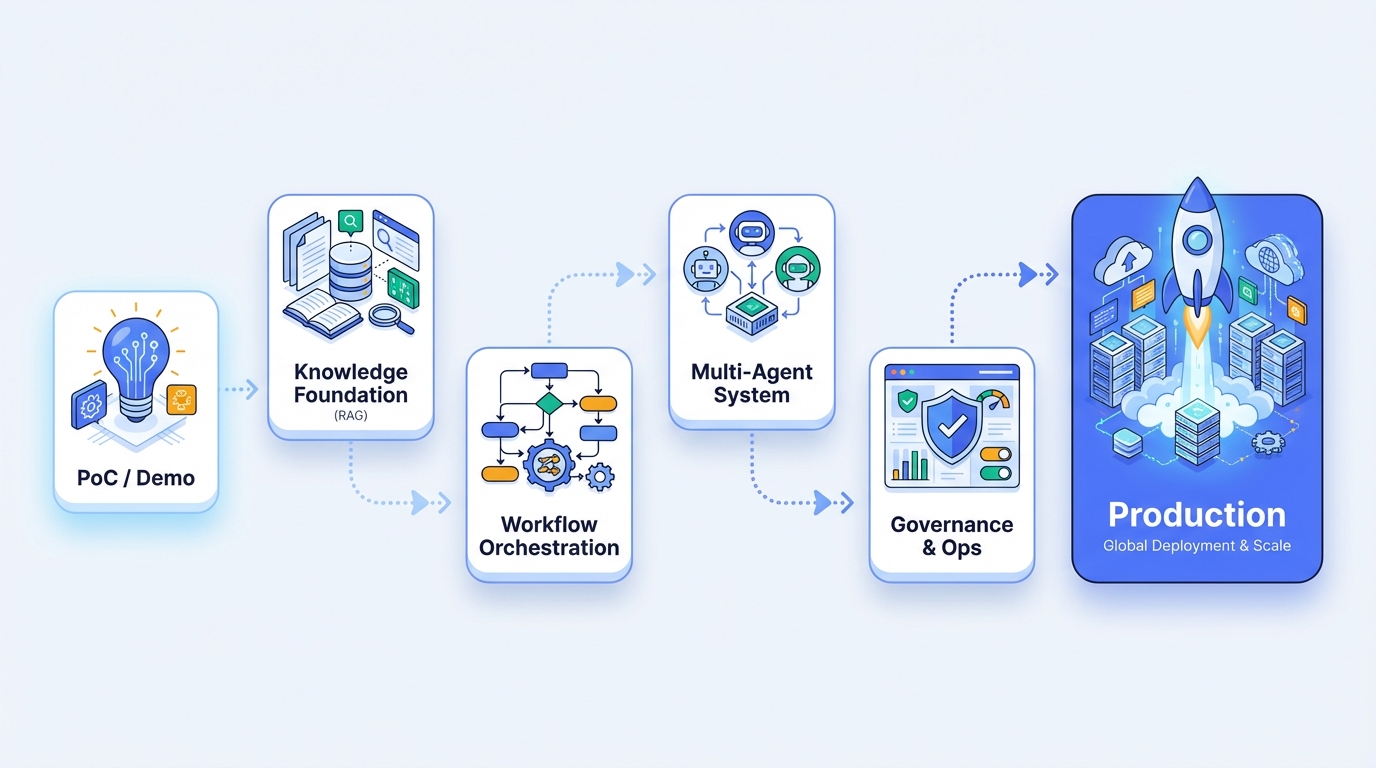
3. The Build Path: From Prototype to Production
Based on deployments across automotive, hospitality, pharmaceutical, and logistics industries, here's the actual path enterprises take:
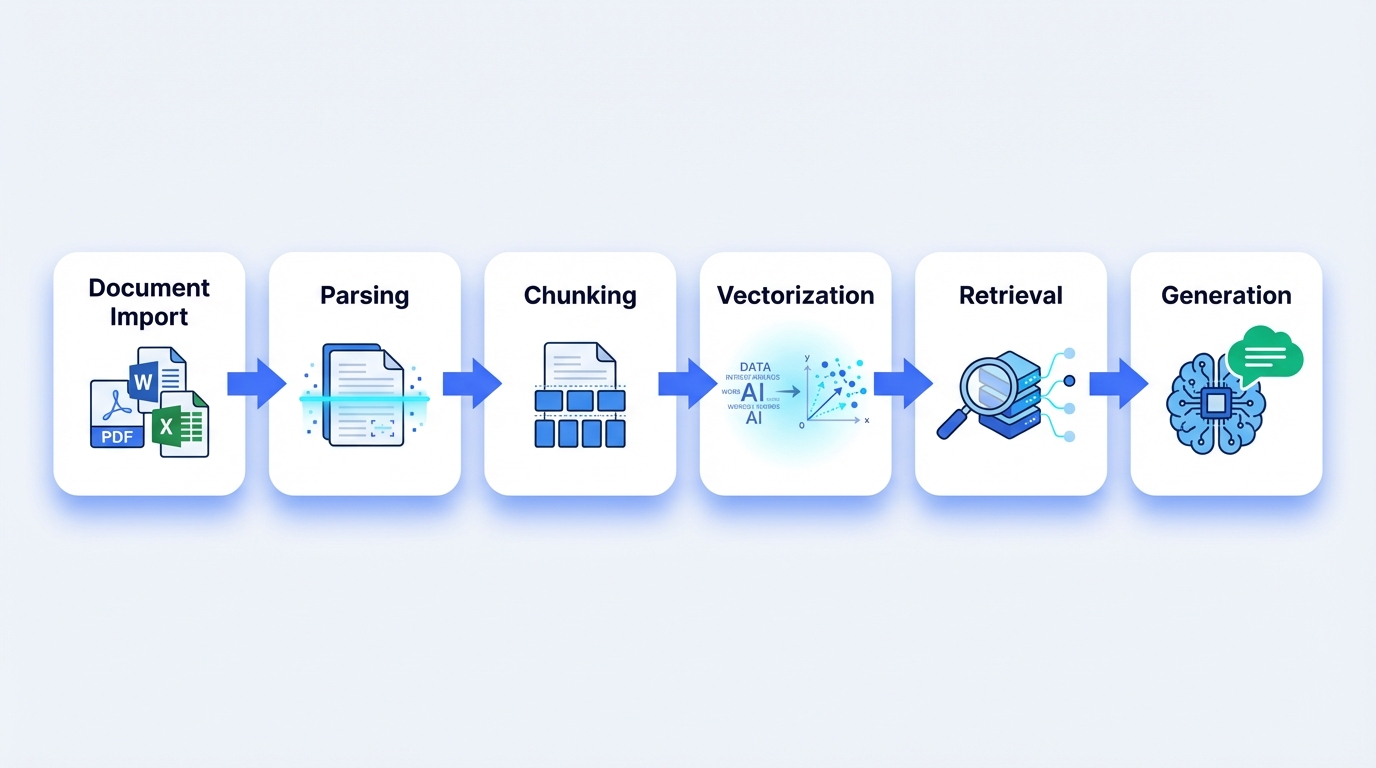
Phase 1: Knowledge Cold Start (RAG Foundation)
The first production blocker is almost always knowledge ingestion. Enterprises underestimate how much effort goes into making documents "agent-ready."
Common failure patterns:
| Failure | What You'll See | What's Actually Wrong |
|---|---|---|
| Format fragmentation | System throws "unsupported file type" error; nested tables in Word docs turn into gibberish | Parser only handles a handful of formats—anything complex breaks |
| Chunking disasters | Agent loses context mid-answer or starts making things up | Text gets mechanically sliced; a coherent explanation ends up in fragments |
| Table blindness | Your Excel data becomes a mess of unstructured text | No multimodal parsing—tables get "flattened" beyond recognition |
| Scale limits | "File exceeds 15MB limit, please compress and retry" | Hard caps on file size; enterprise-scale documents simply won't upload |
What enterprise-grade RAG requires:
- Broad format support: Real enterprises have PDFs, Word docs, Excel sheets, HTML exports, images with embedded text. A production platform must handle 20+ formats without manual conversion.
- Intelligent parsing: Tables, hierarchical headings, and image-text relationships must be preserved—not flattened into unstructured text.
- Multimodal output: When a user asks about a product diagram, the agent should be able to surface the actual image, not just describe it.
A major pharmaceutical retailer consolidated their drug information, IT policies, and HR guidelines into a unified knowledge base. The result: 90% usability rate for drug-related queries and 80%+ reduction in internal support response time.
Phase 2: Workflow Orchestration (Intent + Execution)
Once knowledge is in place, the next challenge is orchestrating how the agent uses it. This is where most "prompt engineering" approaches break down.
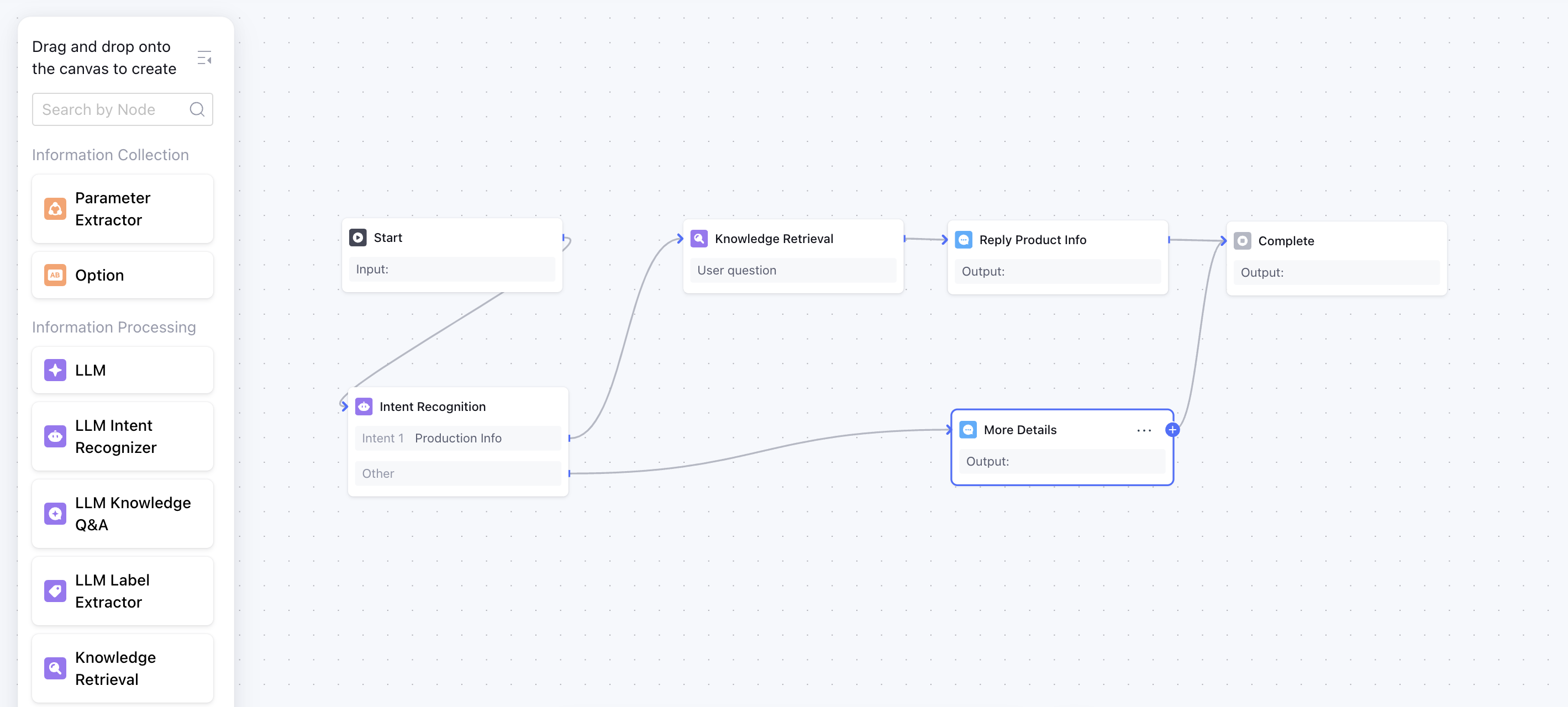
The intent recognition problem:
Consider a restaurant reservation agent. A user says:
"Actually, change it to 7pm instead of 6pm."
A naive agent treats this as a new request. An enterprise-grade agent:
- Recognizes this as a modification to an existing reservation
- Identifies the parameter to change (time: 6pm → 7pm)
- Rolls back to the relevant workflow node
- Executes the change without re-collecting other parameters (date, party size, name)
This requires global intent recognition—understanding user intent across the entire conversation, not just the latest message.
Long-term memory:
Production agents must remember user preferences across sessions. A hospitality group deployed agents that store guest preferences (room type, dietary restrictions, loyalty status) as persistent memory, enabling personalized service without repeated questions.
Workflow node types that matter:
| Node Type | Function | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Parameter Extractor | Pulls structured data from natural language | "Book a table for 4 on Friday" → {party_size: 4, day: Friday} |
| LLM Intent Recognizer | Classifies user intent with reasoning | Distinguish "complaint" vs "inquiry" vs "request" |
| Knowledge Retrieval | Fetches relevant context from RAG | Technical support, policy Q&A |
| Code Node | Executes custom logic | Price calculation, API calls |
| Conditional Branch | Routes based on extracted parameters | VIP vs standard customer flow |
Phase 3: Multi-Agent Collaboration
For complex enterprise scenarios, a single agent isn't enough. But "multi-agent" doesn't mean "multiple prompts"—it requires explicit collaboration patterns.
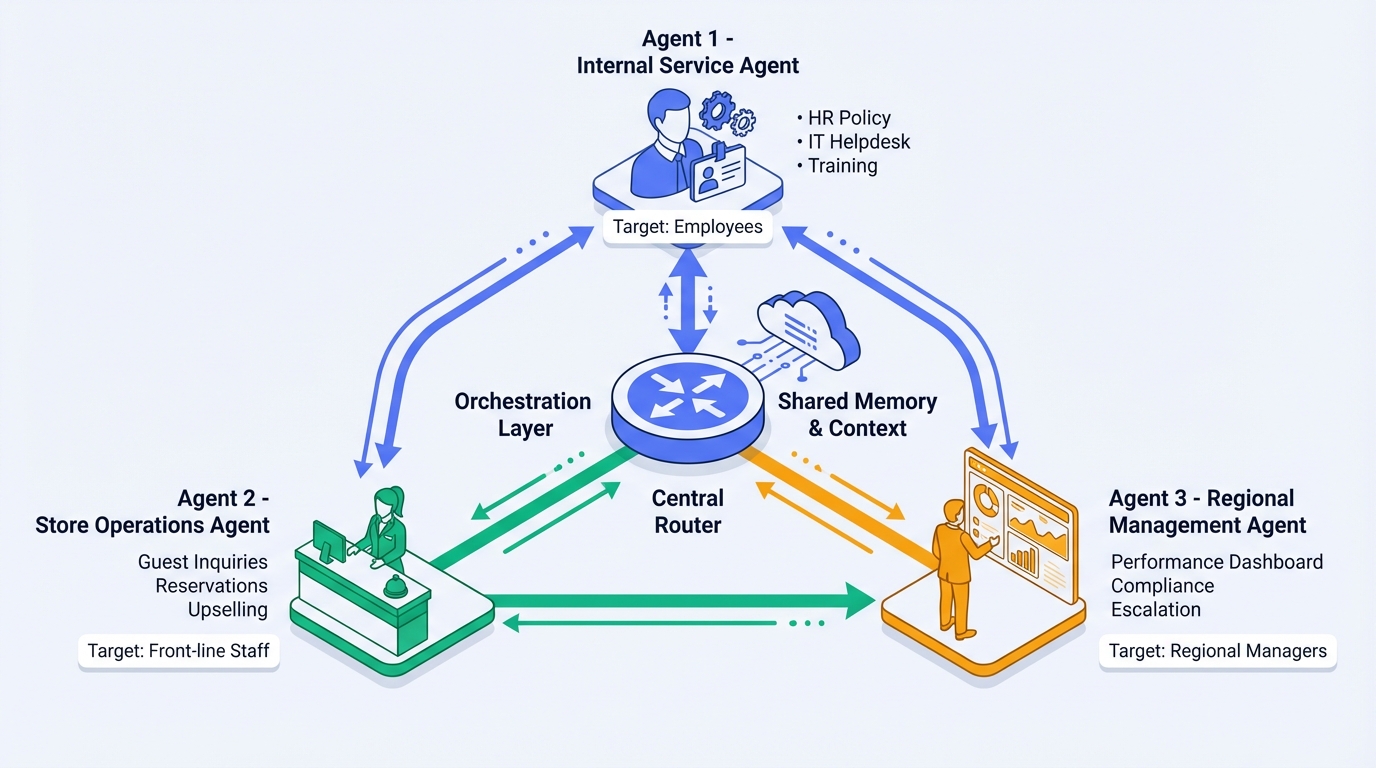
A major hotel group deployed three specialized agents across 5,000+ hotels and 20 brands:
| Agent | Scope | Capabilities |
|---|---|---|
| Internal Services Agent | Employee-facing | HR policy Q&A, IT helpdesk, training materials |
| Store Operations Agent | Front-desk staff | Guest inquiries, reservation management, upselling |
| Regional Management Agent | Area managers | Performance dashboards, compliance checks, escalation handling |
Results:
- Business scenario coverage: 75% → 100%
- FAQ maintenance workload: 1,000+ entries → 100+ entries
- New store manager error rate: ↓60%
- Daily time saved per manager: 0.5–1 hour
Collaboration patterns:
| Pattern | Description | Best For |
|---|---|---|
| Free Handoff | Agents transfer control based on detected intent | Cross-functional queries (e.g., sales → support) |
| Workflow Orchestration | Central workflow routes to specialized agents | Structured multi-step processes |
| Plan-and-Execute | Planner agent decomposes tasks, executor agents handle subtasks | Complex, dynamic problem-solving |
Phase 4: Governance and Operations
The final phase—often ignored until it's too late—is enterprise governance. Production AI agents require:
Cost control:
A dairy company's AI copywriting agent consumes 30 million tokens daily. Without cost visibility and controls:
- Budget overruns are invisible until the invoice arrives
- No way to identify inefficient prompts or runaway loops
- Cannot allocate costs to business units
Security and compliance:
| Layer | Requirement | Implementation |
|---|---|---|
| Data | PII handling, data residency | Encryption, access controls, regional deployment |
| Network | API security, traffic isolation | VPC integration, IP whitelisting |
| Model | Prompt injection defense, output filtering | Guardrails, content moderation |
| Audit | Conversation logging, decision traceability | Immutable logs, explainability features |
Operational resilience:
A logistics company handles 10 million tokens daily through their customer service agent. This requires:
- Distributed cluster deployment for horizontal scaling
- Automatic failover and load balancing
- SLA guarantees (not just "best effort")
4. Agent Builder Platform Comparison
When evaluating AI agent platforms, enterprises should assess capabilities across four dimensions:
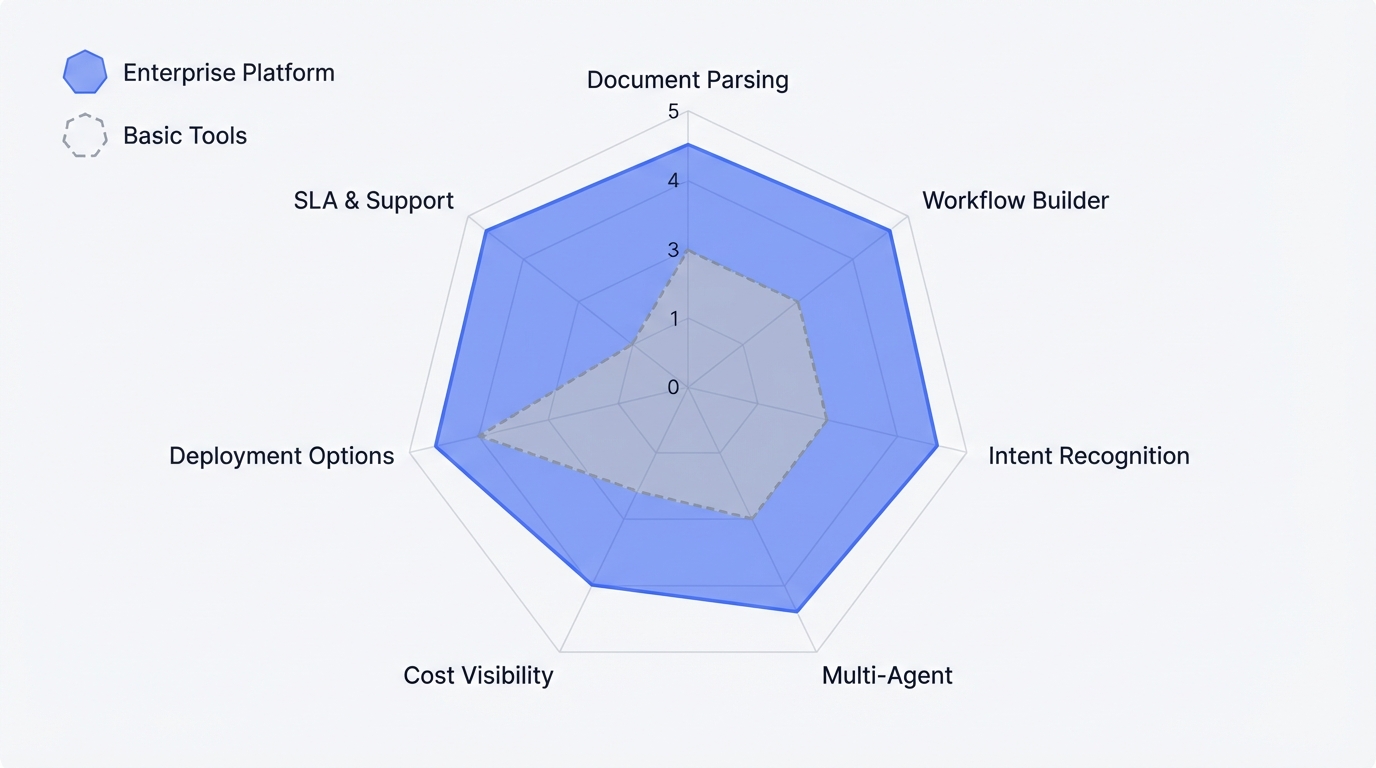
| Capability | Enterprise Requirement | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Document Parsing | 20+ formats, 200MB+ file size, multimodal | Real enterprise data is messy |
| Workflow Builder | Visual editor, conditional logic, code nodes | Business users need to iterate without developers |
| Intent Recognition | Global context, parameter rollback | Users don't speak in single-turn commands |
| Multi-Agent | Explicit handoff patterns, shared memory | Complex scenarios need specialization |
| Cost Visibility | Per-conversation tracking, budget alerts | Finance needs accountability |
| Deployment Options | Cloud, hybrid, private | Compliance requirements vary |
| SLA & Support | Guaranteed uptime, dedicated support | Production systems need guarantees |
Mainstream Agent Builder platform comparison:
| Factor | Open-Source (Dify, n8n, LangChain) | Cloud-Native (Bedrock Agents, Vertex AI) | Enterprise Platform (Tencent Cloud ADP) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Time to Production | Weeks–months (self-build infrastructure) | Days–weeks (integration work required) | Days (visual configuration, ready to use) |
| Operational Burden | High (fully self-managed) | Medium (shared responsibility model) | Low (fully managed service) |
| Customization | High (full code access) | Medium (API-based extension) | Medium-High (visual + code hybrid) |
| Enterprise Support | Community support only | Ticket-based support | Dedicated customer success team |
| Risk Ownership | Fully on enterprise | Shared with cloud provider | Platform provides SLA guarantee |
Selection guidance:
- Dify/n8n: Best for teams with strong technical capabilities and ops capacity, suitable for PoC and internal tools
- Bedrock/Vertex: Best for enterprises already deeply invested in AWS/GCP ecosystems
- Tencent Cloud ADP: Best for scenarios requiring rapid deployment, enterprise-grade SLA, and Southeast Asia/China regional compliance
For an in-depth analysis of platform positioning, see IDC MarketScape 2025: AI Agent Platform Leaders in Southeast Asia
5. Real-World Results
Here's what production deployments actually achieve:

Automotive Manufacturing: Intelligent Customer Service
Challenge: Complex product manuals, slow knowledge onboarding, traditional bots couldn't handle nuanced queries.
Solution: RAG-powered agent with one-click document import, automatic parsing and vectorization.
Results:
- Q&A accuracy: 84%
- Multimodal response rate (images, diagrams): 70%
Want to build a similar customer service agent from scratch? See Build a Customer Service AI Agent in 6 Steps
Hospitality Group: Multi-Agent Operations
Challenge: 30%+ of front desk staff time spent on repetitive questions; 24/7 coverage required expensive staffing.
Solution: Three specialized agents covering internal services, store operations, and regional management.
Results:
- Response accuracy: 95%+
- First-token latency: <5 seconds
- FAQ maintenance reduction: 90%
Pharmaceutical Retail: Internal Shared Services
Challenge: IT, Finance, and HR support requests overwhelming internal teams; drug information scattered across systems.
Solution: Unified knowledge base with enterprise messaging integration.
Results:
- Response time reduction: 80%+
- Drug information usability: 90%
- Customer feedback consolidated: 400,000+ entries for executive decision-making
Logistics: High-Volume Customer Support
Challenge: FAQ maintenance burden, no unified system across channels.
Solution: Workflow-driven agent handling 40+ task types with multi-turn conversation support.
Results:
- Daily token consumption: 10 million (at scale)
- Multi-turn information collection: Enabled complex issue resolution
6. Getting Started
Building enterprise AI agents is a journey, not a one-time project. The path from prototype to production requires:
- Start with knowledge: Get your RAG foundation right before adding complexity
- Design for intent: Build workflows that understand conversation context, not just keywords
- Plan for scale: Multi-agent architectures and governance aren't afterthoughts
- Choose platforms carefully: The gap between demo tools and production-grade Agent Builders is significant
This article is part of the Agent Insights series, exploring how enterprises build, deploy, and govern AI agents in production environments. Ready to move beyond demos?
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is agentic AI? How is it different from AI agents?
Agentic AI refers to AI systems with autonomous planning and execution capabilities. Unlike traditional AI applications, agentic AI can: independently decompose tasks toward a goal, dynamically invoke tools and APIs, handle exceptions during execution, and maintain context across multi-turn conversations. AI agents are the concrete implementation of agentic AI. In 2024, agentic AI became the core direction for enterprise AI deployment, with search volume growing 900% year-over-year.
What is the difference between an AI agent and a chatbot?
A chatbot uses rule-based logic or intent matching to provide scripted responses, best suited for high-volume, predictable queries like order status checks. An AI agent uses LLM-driven reasoning with RAG (Retrieval-Augmented Generation) to handle complex, context-dependent tasks that require autonomous planning and decision-making across unstructured knowledge.
How long does it take to deploy an enterprise AI agent?
Based on real-world deployments, the timeline varies by complexity:
- Simple FAQ agent: 1-2 weeks (knowledge setup + basic workflow)
- Multi-scenario agent: 4-6 weeks (workflow orchestration + intent recognition)
- Multi-agent system: 8-12 weeks (collaboration patterns + governance setup)
The knowledge cold start phase (RAG setup) typically takes 40-60% of total deployment time.
What document formats can enterprise AI agent platforms process?
Enterprise-grade platforms like Tencent Cloud ADP support 28+ document formats including PDF, Word, Excel, PowerPoint, HTML, CSV, TXT, Markdown, and images (PNG, JPG, GIF). File size limits vary—ADP supports up to 200MB per file, compared to ~15MB on many open-source alternatives like Dify.
How do enterprises measure ROI of AI agents?
Key metrics include:
- Efficiency: Response time reduction (typically 60-80%), daily time saved per employee (0.5-1 hour)
- Quality: Q&A accuracy rate (84-95%+), customer satisfaction scores
- Cost: FAQ maintenance reduction (up to 90%), support ticket deflection rate
- Scale: Token consumption, concurrent user capacity, uptime SLA
What are the common failure patterns in enterprise AI agent projects?
The top 4 failure patterns are:
- Format fragmentation: Platform can't process certain document types or complex nested structures
- Chunking disasters: Poor text segmentation leads to hallucination or missed context
- Table blindness: Structured data gets mangled without multimodal parsing
- Scale limits: File size restrictions block large enterprise documents
Can AI agents handle multi-turn conversations?
Yes, enterprise-grade agents support multi-turn conversations with:
- Global intent recognition: Understanding user intent across the entire conversation
- Parameter rollback: Automatically modifying previous parameters without re-collecting all information
- Long-term memory: Storing user preferences across sessions for personalized service
What security measures are required for enterprise AI agents?
Enterprise AI governance requires four security layers:
- Data layer: PII handling, data residency, encryption, access controls
- Network layer: API security, traffic isolation, VPC integration
- Model layer: Prompt injection defense, output filtering, content moderation
- Audit layer: Conversation logging, decision traceability, compliance reporting
How do multi-agent systems work in enterprises?
Multi-agent systems use specialized agents for different functions with explicit collaboration patterns:
- Free Handoff: Agents transfer control based on detected intent
- Workflow Orchestration: Central workflow routes to specialized agents
- Plan-and-Execute: Planner agent decomposes tasks, executor agents handle subtasks
A hotel group example: 3 agents (Internal Services, Store Operations, Regional Management) covering 5,000+ hotels achieved 100% business scenario coverage.

 Home
Home Products
Products Resources
Resources Solutions
Solutions Pricing
Pricing Company
Company Find Us
Find Us
